You are here: CSP Developer’s Guide: Overview > 8 DSP Series 2 Cards Product Description > Redundancy

Introduction
To achieve high reliability, DSP Series 2 cards supports card-level hardware redundancy coupled with dynamic resource allocation.
The DSP Series 2 card offers redundancy in several forms, on several levels:
• DSP resources are pooled, so you can have extra licensed Resource Points available for backup.
• You can store voice files on remote Network File System servers, so the files are not lost if a card fails.
• You can distribute functions types across two or more cards.
• You can use redundant servers with RAID to mirror the content among multiple drives on a server.
Redundancy Through Pooling
The DSP resources on DSP Series 2 cards are pooled. That is, all resources licensed through Resource Points are available to the entire system and are shared over all DSP Series 2 cards. The 4096 DSP Resource Points that come with a two-module card by default (2,048 for a one-module card) are also pooled. However, if a DSP Series 2 card fails, its default Resource Points are subtracted from the pool. The resources attached to a call must be reconfigured by the host application to another DSP Series 2 card.
Because licensed Resource Points are made available to the other DSP Series 2 cards in the CSP, having a surplus of available licensed Resource Points provides another method of redundancy.
Redundancy through Distributed Function Types
Dialogic recommends that you assign the same functions across two or more DSP Series 2 cards, so that if one card fails, the function is still available on another card.
Redundancy through Network File System servers
If a DSP Series 2 card fails, the voice files stored on it are lost from volatile memory. But you can restore those files from a Network File System server. For redundancy and bandwidth considerations, Dialogic recommends using a machine for NFS that is separate from your application host computer. The I/O card is required to use the NFS features.
Redundancy through Multiple Network Files Servers
You can have multiple NFS servers. This is not a 1:1 redundancy scheme, but you can put the same files in two different places, and there is load sharing between the servers.
Redundancy Between Server Drives
There is internal redundancy on each server, because data is mirrored among multiple drives using Raid 5.
Redundancy through the Ethernet ports on the I/O card
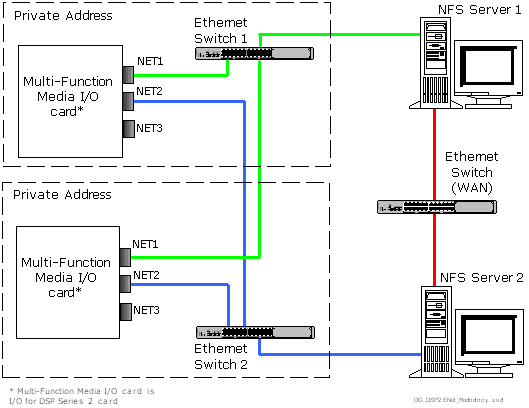
The Multi-Function Media I/O card has three Ethernet ports, NET1, NET2 and NET3, that provide several levels of redundancy. When connecting the I/O card Ethernet ports, the following conditions apply:
• You can connect only one Ethernet port per card to a specific Ethernet switch and associated NFS server.
• If used, each of the other ports on that card must also be connected to a specific Ethernet switch and associated NFS server.
• For each I/O card, if you wanted to use all three Ethernet ports, you would need three Ethernet switches and NFS servers.
The diagram below shows Ethernet ports NET1 and NET2 in use. NET3, although functional, is not being used.
