You are here: CSP Developer’s Guide: Common Channel Signaling > 5 TUP, BT IUP & SSUTR2 > Configuring Virtual CIC Format
Configuring Virtual CIC Format

Purpose
This section describes how to configure the format for TUP Virtual CIC.
Before you begin
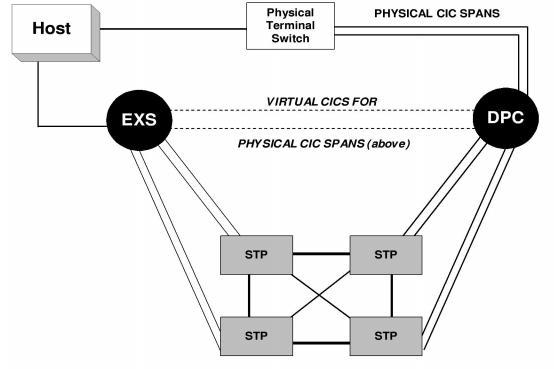
You should be aware that physical CICs can be configured along with Virtual CICs on the same stack.
For TUP Virtual CIC, all API messages use the DPC/Stack/CIC form of addressing instead of time slot addressing in the CSP. SS7 CIC Configure and Service State Configure messages are used. When configuration is finished, the TUP Virtual CIC can generate outbound calls and receive inbound calls, using the PPL Event Indication and the PPL Event Request messages to perform all call processing functions.
As with the Excel China TUP, the TUP Virtual CIC also supports User-Defined messages.
This procedure describes how to configure TUP Virtual CIC in addition to the general CSP configuration.
1 Configure the following in the order listed below:
SS7 Cards - Use the CCS Redundancy Configure message.
Signaling Stacks - Use the SS7 Signaling Stack Configure message.
Signaling Link Sets - Use the SS7 Signaling Link Set Configure message.
Signaling Links - Use the SS7 Signaling Link Configure message.
Signaling Route(s) - Use the SS7 Signaling Route Configure.
2 Assign Virtual Voice Circuits. (Virtual CICs). Use the SS7 CIC Configure message.
3 Bring spans and signaling links in-service. Use the Service State Configure message.
4 Bring Virtual CICs in-service. Use the Service State Configure message with new AIB Address Type.
5 Synchronize actual physical CIC states with Virtual CIC states. Use the L3P TUP PPL (0x11) Event Request 64 for Virtual Span INS status.
6 Assign and configure spans. Use the Assign Logical Span ID and T1/E1 Span Configure messages.
7 Configure SS7 PQ cards. Use the CCS Redundancy Configure message.
8 Configure Signaling Stacks. Use the SS7 Signaling Stack Configure message.
9 Configure Signaling Link Sets. Use the SS7 Signaling Link Set Configure message.
10 Configure Signaling Links. Use the SS7 Signaling Link Configure message.
11 Assign SS7 Virtual Voice Circuits (Virtual CICs). See More on Configuring SS7 Virtual CICs (5-34).
12 Bring spans and signaling links into service. When all the configuration is complete, use the Service State Configure message to establish a connection with the network and to begin call processing. When the destination becomes accessible, the CSP sends the host a PPL Event Indication message. The associated signaling link must be in service for all CICs.
Error Condition: If a host link failure occurs, all virtual CICs that have been configured in the system will be placed Out of Service. The host must then send a Service State Configure message to bring all of those virtual CICs into service.
13 Bring Virtual CICs into service. Send PPL Event Request 64 and Service State Configure to bring Virtual CICs into service. The new AIB Address Type for Virtual CICs is included with both the Service State Configure message and the PPL Event Request 64. When the Virtual CICs come in-service, a PPL Event Indication with Status INS message will be sent for each CIC.

More on Configuring SS7 Virtual CICs
All configuration of Virtual CICs is performed using the SS7 CIC Configure message. Call control, circuit supervision, and maintenance can be managed using the Telephone User Part (TUP) interface.
Assigning CICs to Virtual Voice Circuits
Voice circuits controlled by SS7 Signaling Links are identified by a CIC. A specific voice circuit is identified in the network by its unique DPC-CIC combination.
The SS7 CIC Configure message assigns a DPC/CIC code pair and a User Part (TUP) to virtual voice circuits.
The SS7 CIC Query message is used to retrieve configuration information.
Figure 5-3 Assigning Virtual CICs

The following example shows the SS7 CIC Configure message used to configure a Virtual CIC Group. Each CIC Group can have up to 31 circuits for E1 and 24 circuits for T1.
Byte 23 configures the Call Control User Part as TUP Virtual CIC (0x81).
Trace: H->X FE 00 15 00 6A 00 SN FF 00 01 14 07 00 01 00 00 18 00 01 02 03 01
|
BYTE |
Field |
Value |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
0xFE |
|
|
1-2 |
0x00, 0x16 (22) |
|
|
3-4 |
Message Type (MSB, LSB) |
0x00, 0x6A |
|
5 |
Reserved |
0x00 |
|
6 |
Sequence Number |
0xSN |
|
7 |
Logical Node ID |
0xFF |
|
8 |
AIB Address Method |
0x00 |
|
9 |
Number of Address Elements |
0x01 |
|
10 |
Type |
0x14 |
|
11 |
Data length |
0x07 |
|
12 |
Data [0] Stack ID |
0x00 (Stack 0) |
|
13-14 |
Data [1-2] Base CIC Number |
0x01, 0x00 |
|
15-16 |
Data [3-4] Base CIC Span |
0x00, 0x00 Reserved (should use "0") |
|
17 |
Data [5] Base CIC Channel |
0x00 Reserved (should use "0") |
|
18 |
Data [6] Number of CICs in Group |
0x18 (24 CICs) |
|
19-22 |
DPC |
0x00, 01, 02, 03 |
|
23 |
Call Control User Part |
0x81 (TUP Virtual CIC) |
|
24 |
Checksum |
CS |
Important! Base span number and base channel should not be used and should be "0".
Matrix Controller Switchover after Configuration
During a matrix controller switchover, PPL Event Indications that come from the SS7 card will be lost. Since all the call processing information is sent to the host using PPL Event Indications, the host will lose some call processing data.
After a matrix controller switchover, the host will get PPL Event Indication 400 (0x190) from PPL Component SPRC, containing stack ID, DPC, Base CIC and status for all virtual CICs.
The TUP Virtual CIC supports redundancy for Virtual CICs in the same way that it is currently supported for physical (actual) CICs. There is no change in the configuration of SS7 redundancy.
The System Configuration message allows you to enable and to configure various system maintenance and monitoring features, including:
• Host Link Failure Detection
• System Busy
Host Link Failure Detection and Virtual CICs
The Host Link Failure Detection feature brings all channels or all spans out of service if the CSP detects a failure in the host link. The CSP determines the integrity of the host link by monitoring host ACKs to Poll messages. (You must enable polling to use the Host Link Failure Detection feature.) If the host does not acknowledge two consecutive Poll messages, the CSP begins a timer. If the CSP does not receive a message from the host before expiration of the timer, it resets its Ethernet Receiver.
Upon detection of a host link failure, the CSP responds according to the option set by the host, either to bring all channels out-of-service (0x00) or to bring all channels and spans out-of-service (0x01). The System Configuration message is used to configure both the Response to Host Link Failure (Data[1]) and the Failure Confirmation Timer (Data[2,3]).
During host link failure, all virtual CICs configured in the CSP will be put Out of Service (OOS). The host will have to send a Service State Configure message to bring all those CICs back into service, once the host link failed condition has been corrected.
System Busy Condition and Virtual CICs
A System Busy condition occurs when the CSP is overloaded due to a high volume of call processing traffic. A System Busy alarm is sent to the host when the threshold is reached, indicating that no incoming or outgoing calls can be handled until the condition clears. Although subsequent messages from the host are not necessarily lost, Excel recommends that the host hold back on call processing until the System Busy clears.
During a System Busy condition, the matrix controller will send a message to all the SS7 stacks configured on various SS7 cards to inform about System Busy or System Busy Clear; the appropriate signaling procedure will be initiated to notify the network about the CSP condition. No new incoming calls will be processed during a System Busy condition.
This functionality allows the right SEC message to be sent to the network in response to an incoming call, enabling that call to be cleared.