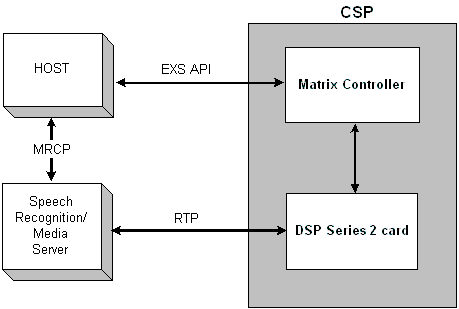
You are here: CSP Developerís Guide: Overview†>†7 DSP Series 2 Card Product Description†>†Media Streaming over RTP

Introduction
RTP, the real-time transport protocol, provides end-to-end network transport functions suitable for applications transmitting real-time data, such as audio, video or simulation data, over multicast or unicast network services. RTP does not address resource reservation and does not guarantee quality-of- service for real-time services.
The DSP Series 2 card supports the direct termination of G.711 u-law RTP streams (payload size: 20 milliseconds) from any third party media server or speech server, required for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Text To Speech (TTS), or any CTI applications using voice recognition.

Configuration
Definitions
The following definitions are taken from RFC 1889, RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications.
RTP Payload
The data transported by RTP in a packet, for example audio samples or compressed video data.
RTP Packet
A data packet consisting of the fixed RTP header, a possibly empty list of contributing sources, and the payload data. Some underlying protocols may require an encapsulation of the RTP packet to be defined. Typically one packet of the underlying protocol contains a single RTP packet, but several RTP packets may be contained if permitted by the encapsulation method.
The abstraction that transport protocols use to distinguish among multiple destinations within a given host computer. TCP/IP protocols identify ports using small positive integers. RTP depends upon the lower-layer protocol to provide some mechanism such as ports to multiplex the RTP and RTCP packets of a session.
Transport Address
The combination of a network address and port that identifies a transport-level endpoint, for example an IP address and a UDP port. Packets are transmitted from a source transport address to a destination transport address.
RTP session
The association among a set of participants communicating with RTP. For each participant, the session is defined by a particular pair of destination transport addresses (one network address plus a port pair for RTP and RTCP).