You are here: CSP Developer’s Guide: Overview > 1 Introduction to the CSP > System Overview
The CSP architecture is a marriage of a distributed hardware environment and an open, programmable software environment.
With the CSP, you can integrate up to seven nodes into a single logical switch.
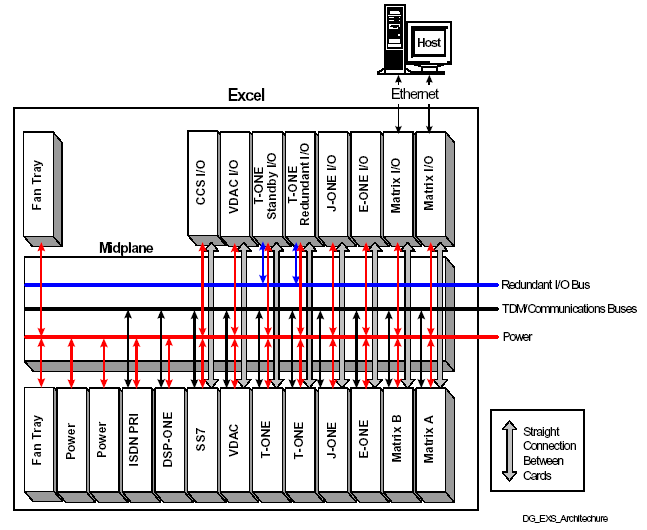
Figure 1-1 An Overview of the CSP Architecture

Open Architecture for Software Development
The open architecture of the CSP provides the following advantages:
• integrates into a wide variety of networks
• supports a wide variety of signaling protocols
• complies with a wide variety of standards
• supports the host computer and a wide variety of operating environments
The CSP has been designed with an open architecture to operate with any host system, any operating system, and any application language. You can write applications independent of network protocols. And you can use the newest, best switching applications from any number of vendors. CSP software includes a rich set of standard Application Programming Interface (API) messages, so no matter how many different applications you use, you receive CSP information in a consistent format.
Open Architecture for Connectivity
The CSP’s rich software environment enables you to:
• Bring new services to market quickly
• Customize your system to support new enhanced services as they emerge
• Adapt to requirements that are specific to a country or region
The CSP’s open software architecture lets you program each port individually. So you can integrate a wide variety of applications with Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and Digital Signal 1(DS1) in many different configurations. The system software also supports rate-compatibility with the Conference of European Postal and Telecommunications (CEPT).
The CSP also lets you connect unrelated resources into the logical switch. For example, you can integrate external voice resources for Interactive Voice Response, Voice Recognition, and Voice over Internet Protocol. The CSP can adapt to changing network protocols and standards worldwide.
The CSP has a modular design, so you can reuse existing components and upgrade to newer technologies without redesigning or scrapping your existing technology. You can start out with a relatively small system, then as your business needs and revenues grow, increase your capacity incrementally. The CSP uses card sub-assemblies so that new chip technologies can be introduced without re-engineering the underlying main board. This modular approach minimizes redesign costs, which we can pass on to our customers.
DSP Resources
The DSP Series 2 card is a high-performance media processing resource that is fully integrated into the CSP, providing a consistent and easy-to-manage integrated telecommunications and media services environment.
The DSP Series 2 eliminates the need for separate voice response units (VRU) by providing powerful media processing services and resources within the DSP Series 2 environment. This also reduces T1/E1 communications, saving service providers both capital expense costs and on-going operating costs.
The DSP Series 2 enables the CSP to operate as a service node or intelligent peripheral. Configured with DSP Series 2 resources, the CSP can be programmed to inter-operate with speech recognition and/or bulk storage to provide a comprehensive media server solution. The CSP supports Network File System (NFS) with on-board cache for voice file storage.
See the DSP Series 2 CardProduct Description chapter.