This section describes supplementary services related to call forwarding. Call forwarding is a service performed at a served user (or on behalf of a served user) to reroute a call to another user. This topic describes:
The following services are related to call forwarding:
|
Service |
Description |
|
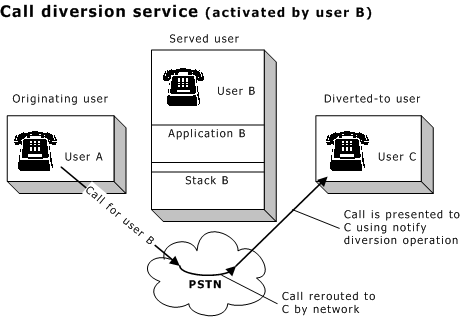
Call diversion |
Calls addressed to a served user are rerouted (forwarded) to a different address by the network, on behalf of the served user. Available under ETS 300 and Q.SIG. Call diversion services can work in any of three ways: Call forwarding - no response (CFNR). Calls can be rerouted to a different user if the originally addressed user fails to answer the call within a certain interval. Call forwarding - busy (CFB). Calls can be rerouted to a different user if the originally addressed user is currently in a call (for example, the line is busy). Call forwarding - unconditional (CFU). Calls can be rerouted to a different user unconditionally. |
|
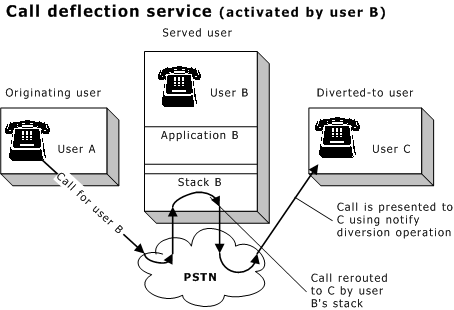
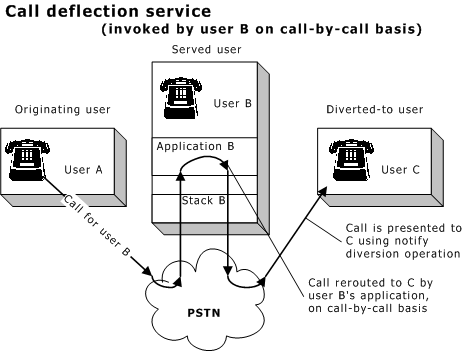
Call deflection |
Allows the served user's stack or application to forward a call to a different address. Available under ETS 300 only. |
|
Remind diversion |
When a served user initiates an outbound call, this service informs the served user if call diversion services are activated for incoming calls. Available under ETS 300 only. |
In an ETS 300 application, call forwarding can be accomplished in any of three ways, depending upon which entity the served user performs the forwarding operation (see the following illustrations):
The served user application can activate or deactivate the call diversion service for a particular user address. Call diversion takes place at the network level. From then until the service is deactivated, if a call arrives for the user, the network reroutes the call to another user.
The served user application can activate or deactivate the call deflection service for one or more NAIs. When activated, call deflection takes place in the stack. From then until the service is deactivated, all calls on those NAIs are rerouted to another user.
The served user application can invoke the call deflection service on a call-by-call basis. When the service is invoked in this way, temporary activation of the service occurs implicitly.
Regardless of which service is used, the diverted-to user is always notified of a forwarded call using a notify diversion operation.
The served user application can enquire the network for the status of the call diversion service for a given user, or for all users.
The remind diversion service can be invoked by the network if the user has subscribed to this service. When a served user initiates an outbound call, this service informs the served user if call diversion services are active for incoming calls.

In a Q.SIG application the call forwarding process is as follows:
The served user node invokes the call diversion service to request the originating node to forward a call.
The originating node offers the call to the diverted-to user node, performing a notify diversion operation to notify the node that the call has been forwarded from another user.
The Remind diversion service (ETS 300) describes how an application can perform these procedures. Since the application may be associated with the originating node, served user node, or diverted-to node, all three perspectives are considered.
Note: Q.SIG specifications identify a fourth party involved in a diversion: the node responsible for rerouting the call (the rerouting node). NMS ISDN supports the combination of the originating and rerouting nodes in the same node (for example, call diversion by rerouting). It does not support the combination of rerouting node and served user node (for example, call diversion by forward transfer).
Call deflection supplementary services are not applicable to Q.SIG applications since there is no user side of a Q.SIG link.