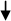 ADICMD_START_PROTOCOL (=13001) src=2000 dst=1 s1=60 d1=12f8c8 s2=e0 d2=0 s3=78002907 d3=0
ADICMD_START_PROTOCOL (=13001) src=2000 dst=1 s1=60 d1=12f8c8 s2=e0 d2=0 s3=78002907 d3=0This topic describes:
Use ctdaemon to:
Modify system global default parameters, set the global trace mask, perform remote tracing with a Java applet, and optionally log trace messages to a file.
Create and manage processing contexts on behalf of the applications and enable applications to share and hand off server resources.
ctdaemon [option]
Where Windows options are:
|
Windows option |
Use this option to... |
|---|---|
|
-f filename |
Specify an ASCII file containing statements for defining services and service managers and overriding default parameters. Usually this file is cta.cfg. |
|
-i |
Run ctdaemon as an interactive console application. |
|
-? or -h |
Access help. |
Where UNIX options are:
|
UNIX option |
Use this option to... |
|---|---|
|
-f filename |
Specify the ASCII configuration file containing statements for defining services and service managers and overriding default parameters. Usually this file is cta.cfg. |
|
-i |
Run ctdaemon as an interactive console application. |
|
-q |
Run ctdaemon in quiet mode (as a non-interactive console application). This mode is the default if no option is specified. |
|
-s |
Stop the currently running, non-interactive ctdaemon session. |
|
-k |
Deallocate global objects created by previous executions of ctdaemon. |
|
-? or -h |
Access help. |
ctdaemon performs the following actions:
|
Step |
Action |
|
1 |
Reads the configuration file specified on the command line or finds cta.cfg in CTA_DPATH (defined during installation). |
|
2 |
Passes the services and service managers specified in the [ctasys] section of the cta.cfg to the call to ctaInitialize. |
|
3 |
Places the compile-time parameter values in shared memory to be modified after service initialization. |
|
4 |
Reads the [ctapar] section of the configuration file and writes new parameter values into shared memory. |
Under Windows, when you reboot your system following the Natural Access installation, the Natural Access Server (ctdaemon) starts automatically as a Windows service. If the service is not running, you can start it in one of the following ways:
Access a command prompt and enter:
net start ctdaemon
In the Windows Control Panel, double-click on Services and start the NMS CT daemon service.
Under UNIX, invoke ctdaemon -i from the command prompt. This method allows full console interaction with ctdaemon.
Applications that use system global default parameters retrieve default parameter values from shared memory instead of retrieving compile-time process global defaults from the process data area.
To use system global default parameters, an application must:
Specify in cta.cfg all Natural Access services used by the application. For example, cta.cfg must be modified as shown to allow a fax application to use the system global default parameters:
Service = nfx, nfxmgr
Set the parmflags field of the CTA_INIT_PARMS structure passed to ctaInitialize to CTA_PARM_MGMT_SHARED. If this bit is chosen and ctdaemon is not running, CTAERR_SHAREMEM_ACCESS is returned. Since an error is not returned if ctdaemon crashes, parmflags cannot be used to check ctdaemon.
If an application wants global default parameters to be stored in shared system memory but does not want an error to be returned if ctdaemon is not running, set parmflags to CTA_PARM_MGMT_SHARED_IF_PRESENT. If this setting is chosen and ctdaemon is not running, the default parameter management is local to the process.
When you start ctdaemon in a command window, you can use it to retrieve and modify global default parameter values. For example:
Enter s parmname = value or g parmname to modify (set) or retrieve (get) the current default value.
Enter ? at the interactive command prompt to display the available commands.
To generate a list of parameters that can be used in the [ctapar] section of the configuration file, use the ctaparm utility. Refer to Natural Access parameter display: ctaparm. Edit the parameters that have different default values and place them in cta.cfg.
ctdaemon holds a shared memory segment for tracing. To enable tracing from applications, ctdaemon must be running and the traceflags field of the CTA_INIT_PARMS structure passed to ctaInitialize must be set to CTA_TRACE_ENABLE.
Trace messages display only if the trace mask corresponding to the specific type of message is enabled. To instruct ctdaemon to set the global trace mask, use the m tracemask command from the ctdaemon command line. This command sets the trace mask for all processes that enabled tracing with ctaInitialize. To be more selective in tracing, use ctaSetTraceLevel from the application itself to set the trace mask for a specific context in a specific process.
Specify the trace mask as a sequence of strings delimited by + signs (with no spaces). Each string corresponds to a trace mask value that you can specify in ctaSetTraceLevel.
Note: On UNIX systems, Natural Access Server (ctdaemon) must be running to provide board resources for Natural Access applications. If ctdaemon stops running, stop any Natural Access applications that are performing tracing or using global default parameters before restarting ctdaemon.
Enter d at the interactive command prompt to see recognized names for setting the trace mask:
|
String |
Trace mask value |
|---|---|
|
all |
CTA_TRACEMASK_ALL |
|
allcmd |
CTA_TRACEMASK_ALL_COMMANDS |
|
allevt |
CTA_TRACEMASK_ALL_EVENTS |
|
drvcmd |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DRIVER_COMMANDS |
|
drvevt |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DRIVER_EVENTS |
|
dispcmd |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DISP_COMMANDS |
|
dispevt |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DISP_EVENTS |
|
apicmd |
CTA_TRACEMASK_API_COMMANDS |
|
apievt |
CTA_TRACEMASK_API_EVENTS |
|
apierr |
CTA_TRACEMASK_API_ERRORS |
|
svcerr |
CTA_TRACEMASK_SVC_ERRORS |
|
dbgbit0 |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DEBUG_BIT0 |
|
dbgbit1 |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DEBUG_BIT1 |
|
dbgbit2 |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DEBUG_BIT2 |
|
dbgbit3 |
CTA_TRACEMASK_DEBUG_BIT3 |
|
cltcmd |
CTA_TRACEMASK_CLNT_COMMANDS |
|
cltevt |
CTA_TRACEMASK_CLNT_EVENTS |
|
svrcmd |
CTA_TRACEMASK_SRVR_COMMANDS |
|
svrevt |
CTA_TRACEMASK_SRVR_EVENTS |
|
none |
0 |
To view the trace messages that are made available by ctdaemon:
Open the trace file. The TraceFile keyword in cta.cfg specifies the name of the trace file. Trace messages are appended to the trace file each time ctdaemon is started. You must delete or archive this file as necessary.
Use the local console.
Note: When running the Natural Access Server, view trace messages from the trace file.
From a remote location, use the remote trace utility
and a Java 1.1-capable web browser. Refer to Remote trace utility: rtrace for details
about using the remote trace utility.
Refer to Managing
parameters and Handling Natural Access errors for more information.
ctdaemon generates the following output:
Trace timestamp.
Generic trace information (valid for all trace messages).
Note: All values are in hexadecimal format unless otherwise noted.
The timestamp displays as follows:
Wed Dec 24 21:40:01 2003
The timestamp indicates when the event was logged.
The generic trace information displays as follows:
| pid=ce tid=ba ctahd=80000001 (CTATEST) uid=0 tag=4005 sev=0
Generic trace information includes:
|
Field |
Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
pid |
Identifier of the process that logged trace messages. | ||||||||
|
tid |
Identifier of the thread in the process that logged the trace message. This information is not valid on non-threaded operating systems. | ||||||||
|
ctahd |
Identifier of the context for which the trace message was logged. (The context ID is an arbitrary string passed to ctaCreateContext.) | ||||||||
|
text in parentheses |
Name of the context for which the trace message was logged. | ||||||||
|
uid |
User ID specified when creating the context for which the trace message was logged. | ||||||||
|
tag |
Numeric value of trace type tag. This value determines how information pertaining to this trace message is formatted. The standard trace types are explained later in this section. | ||||||||
|
sev |
Severity of the error. Refer to CTA_TRACE_SEVERITY in ctadef.h. Valid values include:
|
Type-specific trace information pertains to the following types of objects that are being traced:
Command information displays as follows:
| 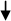 ADICMD_START_PROTOCOL (=13001) src=2000 dst=1 s1=60 d1=12f8c8 s2=e0 d2=0 s3=78002907 d3=0
ADICMD_START_PROTOCOL (=13001) src=2000 dst=1 s1=60 d1=12f8c8 s2=e0 d2=0 s3=78002907 d3=0
Command information includes:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays under Windows only. |
|
Name |
Name of the command sent to the dispatcher. |
|
Number in parentheses |
Numeric value of the command. |
|
src |
Source service identifier. Service identifier values are defined in their respective service header files (for example, adidef.h or ctadef.h). |
|
dst |
Destination service identifier. In this example, the destination of 1 corresponds to ADI_SVCID. Service identifier values are defined in their respective service header files (for example, adidef.h or ctadef.h). |
|
s1 |
Size of the first buffer associated with this command. |
|
d1 |
Address of the first buffer associated with this command. |
|
s2 and d2 |
Size and address of the second buffer associated with the command. |
|
s3 and d3 |
Size and address of the third buffer associated with the command. |
You can retrieve information about events generated by the dispatcher and events generated by the application. The event information displays as follows:
| 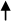 CTAEVN_DISP_OPEN_SERVICE_DONE (10002111) Finished (val=1001) src=1
CTAEVN_DISP_OPEN_SERVICE_DONE (10002111) Finished (val=1001) src=1
dst=1000 time=df8ee5ce uid=0 size=7c buf=421a90
Event information includes:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays under Windows only. |
|
Name |
Name of the dispatcher event. |
|
Number in parentheses |
Event ID value. |
|
String |
Text associated with the reason code for this event. |
|
val |
Value of the dispatcher event. |
|
src |
Source identifier of the service that caused this event to be sent to the dispatcher. |
|
dst |
Destination service identifier to which this event was sent. |
|
time |
Timestamp that the dispatcher associates with the event. Compare timestamps with other events to determine the order in which events were generated. |
|
uid |
User identifier (0) of the context that caused this event to be generated (ctaCreateContext). |
|
size |
Size of the event-specific buffer associated with this event. |
|
buf |
Address of the event-specific buffer associated with this event. |
You can retrieve error information from ctdaemon. Errors can appear as:
| ERR: CTAERR_INVALID_STATE (=c) d1=0 d2=0 txt= fn=adiStartProtocol ln=0 file=
Error information includes:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Name of the error. |
|
Code in parentheses |
Value of the error code. |
|
d1 and d2 |
Error-specific buffers associated with the error. |
|
fn |
Name of the function that generated this error. |
|
ln |
Line number in the source file for the function that generated the error. If ln=0, then the function that generated the error did not specify a line. |
|
file |
Name of the source file for the function that generated the error. If file= is blank, the function that generated the error did not identify its source file. |
If you explicitly call ctaLogTrace with a tracetag value of CTA_TRACETAG_STRING, the string displays as:
| debug_string
If you explicitly call ctaLogTrace with a tracetag value of CTA_TRACETAG_DWORD, the value displays as:
| DWORD: 10 (0xa)
The first number is the decimal value of the DWORD. The value in parentheses is the hexadecimal value of the DWORD.
If you explicitly call ctaLogTrace with tracetag value of CTA_TRACETAG_INT32, the value displays as:
| INT32: 10 (0xa)
The first number is the decimal value of the 32-bit integer. The value in parentheses is the hexadecimal value of the DWORD.