Network management allows administrators to maintain network integrity. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an industry standard protocol that defines a method for performing network management. SNMP was initially made available for IP-based enterprise networks, and is now available for telephony networks.
An SNMP network management system consists of:
One or more managed nodes, running one or more SNMP agents. An agent keeps information about its managed node in a database called a management information base (MIB).
One or more network management stations, running network management software and displaying network information. The management station is called the host.
A network management protocol that determines how the managed node and the management station communicate over the network.
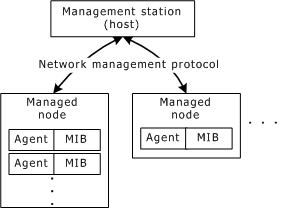
The following illustration shows the relationship between the SNMP components:

In this illustration, one management station is shown communicating with two managed nodes. The first managed node has more than one agent, and each agent has its own MIB. The dotted lines in the managed node show that there can be more agent/MIB pairs running on a managed node. The dotted lines to the right of the managed nodes show that there can be additional nodes managed by a single management station.
An object identifier (OID) is a unique sequence of integers that represent how to traverse the MIB tree to access a managed object. All MIBs have a common root node. All OID integer sequences start from that root. The OIDs are assigned by the IETF.
The tree of MIBs is referred to as a namespace. Each MIB and OID is unique. The namespace for the tree is maintained by the IETF and related organizations, who delegate authority only for MIBs below the Enterprise's MIB, whose OID is 1.3.6.1.4.1.