You are here: CSP Developer’s Guide: Common Channel Signaling > 12 V5.2 Protocol > V5.2 Startup

Purpose
This section describes the automated V5.2 Startup Types.
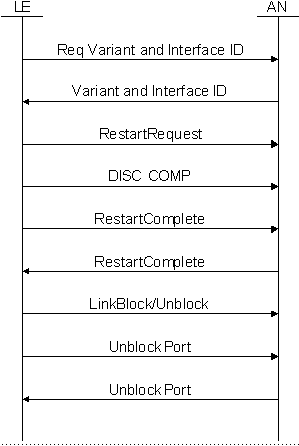
The V5 startup procedures vary, depending upon what the LE side and AN side support for port alignment procedures and restart procedures. Two startup sequences are shown below:
• Typical Startup Sequence
• Typical Startup Sequence with Accelerated Port Alignment
1 Refer to the desired startup sequence diagram on the next page.
2 Initiate the request for the variant ID and interface ID.
Important! This request has a unique control element ID and is used in Common Control messages. The purpose is to verify that the LE side and AN side are communicating about the same interface and running the same variant. The variant is a number in the range 0-127, that the LE side and AN side agree upon at provisioning.
3 Continue with the startup sequence, if the request for the variant ID and interface ID is successful.
The the flow diagrams below represent typical startup sequences. They do not show the actual messages that carry the information.
• The Common Control message is used for the Req Variant and Interface ID and the restart messages.
• The Disconnect Complete message is used for all of the configured user ports.
• The Unblock Port is a Port Control message.
• All of the messages are individually acknowledged (not shown).
• A PPL Config. Byte enables the restart procedure (see the PPL Developer’s Guide). This is defaulted for the LE.
• At the end of the restart procedure is an option for choosing whether to send no link blocking and unblocking commands, to block only the links that were previously blocked, or to send the blocking and unblocking commands for each configured link.
4 Once the procedure is finished, the host receives a PPL Event Indication message indicating that startup is complete.
Important! Please see the Appendix for additional Call Flows pertaining to startup (Call Flows numbered 1-5).

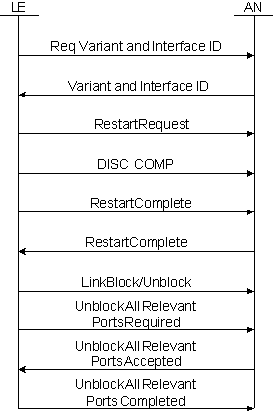
Typical Startup Sequence with Accelerated Port Alignment
In the Typical Startup Sequence diagram above, it takes longer for all of the messages to propagate back and forth during this procedure.
• To speed startup, the Accelerated Port Alignment procedure is shown below.
• Instead of unblocking all ports individually, a new set of Common Control messages are sent that unblock all relevant ports.
• Then, either side can selectively block the user ports that it needs to block.