You are here: CSP Developers Guide: Common Channel Signaling > 4 SS7 Call Control for ISUP > Important ISUP PPL Information
Important ISUP PPL Information

Overview
This section highlights some of the more important ISUP PPL components information related to SS7 customization. Complete Configuration Byte values, and PPL timers and events are documented in the SS7 PPL Information of this guide.
This section identifies important PPL Configuration Bytes for each component, and their default values.
The L3P CIC PPL Configuration Bytes configure the following:
Bytes 1-3 - CGB, CGU, GRS
Point to the byte locations of the Circuit Group Block (CGB), Circuit Group Unblock (CGU), and Circuit Group Reset (GRS) parameters, which are used when generating group messages. Other functions in the system access these parameters. You can move the location of the parameter values within the L3P CIC Configuration Bytes; however, you must update Bytes 1-3 to point to their location.
Bytes 4-7 - SS7 Parameter Information For Outgoing Calls
Required when the host sends BCD-encoded digits.
Byte 8 - Request For Service With Data message format
For incoming calls. Address information can be passed as SS7 parameter data or as BCD-encoded digits.
Byte 9
Determines if an incoming SS7 call requires a response with the ACM/ANM or CON messages.
Byte 10 - Host Out-of-service and In-service Operation Flag
This flag determines if a reset or block/unblock sequence is used for host initiated out-of-service and in-service transitions.
Bytes 15-145 - Values For SS7 Parameters In Outgoing Messages
These values are used unless the host overrides them in an SS7 Parameters ICB. Values are included for the following messages:
|
Message |
Value |
|---|---|
|
ACM |
Address Complete Message |
|
ANM |
Answer Message |
|
BLO |
Blocking |
|
CGB |
Circuit Group Blocking |
|
CGU |
Circuit Group Unblocking |
|
CON |
Connect Message |
|
CPG |
Call Progress |
|
GRS |
Circuit Group Reset |
|
IAM |
Initial Address Message |
|
REL |
Release |
|
UBL |
Unblocking |
The ISUP CPC Configuration Bytes contain values for the Dual-seizure Control Flag and CPC-initiated REL parameters.
Byte 1 - Dual-seizure Control Flag
Upon detection of a dual-seizure condition (collision between incoming and outgoing IAMs); this flag determines which side is dropped.
Bytes 1016, 2531, and 4046 - parameter values for CPC-initiated Releases, depending on the failure reason
Under certain circumstances, ISUP CPC must initiate a release to the network. For example, expiration of the T8 timer results in a forward REL with a Cause Value of "Temporary Failure" ITU ISUP SPRC.
Byte 1 - Range & Status Parameter ID
This ID is required for logic in ISUP, which identifies group messages and routes them to the correct group state machine based on the value of the range field.
Byte 2 - Byte Offset of the Range Field
The range field of the Range and Status parameter is assumed to be one octet. However, its placement in the Range and Status parameter is not assumed. This Configuration Byte entry contains the byte offset into the parameter for the range field (this is 0 for ITU). This is done, along with the Range and Status parameter name, in order to allow ISUP to be able to handle ISUP message and parameter variants.
Byte 3 - ITU Service Indicator
This field is placed in to every outgoing ISUP message as a field in the MSU Service Information Octet.
Byte 4 - ITU Subservice Field
This field is placed into every outgoing ISUP message as a field in the MSU Service Information Octet.
Byte 5 - MTP Pause Logic Flag
After an MTP Pause indication is received, the SPRC can either process the pause immediately, or it can delay the pause processing and queue any outgoing messages to MTP. If an MTP Resume indication is received before timer expiration, the queued messages are sent to MTP. If the timer expires, the queued messages are discarded and the pause is processed. (For a description of ISUP MTP Pause Logic, see ISUP MTP Pause Logic Options
ANSI L3P CIC
Bytes 1 and 3 - CGB, CGU, and GRS
Point to the byte locations of the Circuit Group Block (CGB), Circuit Group Unblock (CGU), and Circuit Group Reset (GRS) parameters, which are used when generating group messages. These parameters are accessed by other functions in the system. The location of the parameter values can be moved within the L3P CIC Configuration Bytes, however, Bytes 1 and 3 must be updated to point to their location.
Bytes 4-7 - SS7 parameter information
Required for outgoing calls when the host sends BCD-encoded digits in an Outseize Control message.
Byte 8 - Request For Service With Data message format
For incoming calls. Address information can be passed as SS7 parameter data or as BCD-encoded digits.
Byte 10 - Host Out-of-service And In-service Operation Flag
This flag determines if a reset or block/unblock sequence is used for host initiated out-of-service and in-service transitions.
Bytes 15-137 - SS7 Parameter Values For Outgoing Messages
These values are used unless overridden by the host in an SS7 parameters ICB.
The ISUP CPC Configuration Bytes control the Dual-Seizure Control Flag and CPC-initiated REL parameters.
Byte 1 - Dual-Seizure Control Flag
Upon detection of a dual-seizure condition (collision between incoming and outgoing IAMs); this flag determines which side is dropped.
Bytes 1016, 2531, 4046, and 5161 - parameter values for CPC-initiated Releases, depending on the failure reason.
Under certain circumstances, ISUP CPC must initiate a release to the network. For example, expiration of the T8 timer results in a forward REL with a Cause Value of "Temporary Failure."
ISUP SPRC PPL Configuration Bytes control configuration flags, messages, and other important values, as follows:
Byte 1 - Range & Status Parameter ID
This ID is required for logic in ISUP which identifies group messages and routes them to the correct group state machine based on the value of the range field.
Byte 2 - Byte Offset of the Range Field.
The range field of the Range and Status parameter is assumed to be one octet. However, its placement in the Range and Status parameter is not assumed. This Configuration Byte entry contains the byte offset into the parameter for the range field (this is 0 for ANSI). This is done, along with the Range and Status parameter name, in order to allow ISUP to be able to handle ISUP message and parameter variants.
Byte 3 - ANSI Service Indicator
This field is placed in to every outgoing ISUP message as a field in the MSU Service Information Octet.
Byte 4 - ANSI Subservice Field
This field is placed into every outgoing ISUP message as a field in the MSU Service Information Octet.
Byte 5 - MTP Pause Logic Flag
Upon reception of an MTP Pause indication, the SPRC can either process the pause immediately, or it can delay the pause processing and queue any outgoing messages to MTP. If an MTP Resume indication is received before timer expiration, the queued messages are sent to MTP. If the timer expires, the queued messages are discardedISUP MTP Pause Logic Options.
Bytes 6-26 - SPRC-initiated Confusion
CFN messages to the network in response to an unrecognized or corrupt message.
Bytes 30-32 - parameter values for an Unequipped CIC
UCIC message to the network in response to a network message that pertains to an unknown or out-of-service CIC.
L3P CIC PPL Configuration Bytes
The mapping of the PPL Configuration Bytes for the L3P CIC component allows you to move Configuration Bytes for a message without modifying the PPL protocol.
Existing atomic functions point to specific Configuration Bytes for the format information on a specific message. If this information was moved to a new Configuration Byte location, the DSD would have to be updated to reflect the new location of the Configuration Bytes.
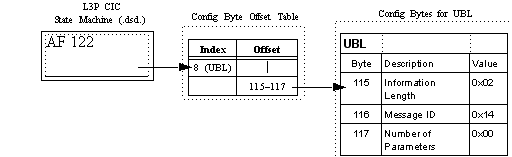
There are three blocks of 200 Configuration Bytes each, for a total of 600 Configuration Bytes. Bytes 501600 are used as the Configuration Byte Offset Table, which contains an index pointing to the location of the Configuration Bytes with the format information for each message.
Atomic Function 122 in the L3P CIC state machine points to the index in the Configuration Byte Offset Table, which indicates the location of the Configuration Bytes for a specific message. If you move the location of the Configuration Bytes for a message, you only need to update the Configuration Byte Offset Table, using the PPL Configure message, to reflect the new location.
The next figure shows the usage of the Configuration Byte Offset Table by the L3P CIC state machine to access Configuration Bytes for a specific message. See SS7 PPL Information for ITU and ANSI Configuration Byte offset values.
Figure 4-10 Use of Configuration Byte Offset Table

Each PPL component has multi-purpose timers, which you can activate at any time. Each component using timers has a table that contains information on specific timers (name, value). When a protocol requires a timer, an atomic function is initiated to activate one of the PPL timers and to point to an index in the components timer table, which contains the value for the required timer. See SS7 PPL Information in this manual for default timer values.
The table below lists other common SS7 customization which is implemented through modification of PPL Configuration Bytes with the PPL Configure message.
|
To modify... |
Use... |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
Component |
Config Bytes |
|
Host-initiated Out-of-Service Logic Flag |
L3P CIC |
10 |
|
Dual-seizure (Glare) Control Flag |
ISUP CPC |
1 |
|
Default Outgoing SS7 Parameters |
L3P CIC |
All |
|
Service Indicators |
ISUP SPRC |
3 |
|
Subservice Field |
ISUP SPRC |
4 |
|
Range and Status Parameter ID |
ISUP SPRC |
1 |
|
CFN Parameters- ANSI only |
ISUP SPRC |
All |
|
ISUP CPC Initiated Release Parameters |
ISUP CPC |
All |
|
ITU CON/ANM/ACM Control |
ITU L3P CIC |
9 |
|
Transmitted LSSU Status Field |
MTP2 TXC |
All |
|
Network Indicators |
MTP3 HMDT and |
All |