You are here: CSP Developers Guide: Internet Protocol > 8 H.323 Software > Software Overview

The H.323 VoIP Gateway complies with H.323 Version 2.0, and therefore supports all gateway Registration, Admission, and Status (RAS) functions.
The H.323 VoIP Gateway provides an interface between the PSTN and IP network for voice calls. IP-to-IP calls are also supported on the gateway. The H.323 stack is implemented on the specially-configured IP Signaling Series 3 card. The IP Signaling Series 3 card has a special software load that includes IP Signaling interface support and the H.323 stack.
Assuming adequate network conditions, the CSP delivers carrier-class voice quality over H.323.
The CSP H.323 offering on the CSP provides both signaling and media capability, so application developers do not need to add these features separately. The H.323 signaling is provided by the IP Signaling Series 3 card and media is provided by the VDAC-ONE or IP Network Interface Series 2 card.
Seamless PSTN-IP Signaling Interworking: SIP/H.323/SS7/ISDN
This H.323 implementation uses Universal Protocol Data Format (UPDF) to provide seamless protocol interworking, with no need for protocol-specific messages. This interworking includes calls from PSTN-to-PSTN, IP-to-IP, PSTN-to-IP, and IP-to-PSTN.
The User Input Indication (UII) message is available in the CSP to transmit inputs from the user interface to the receiver. The inputs could be a button that the user presses on the PSTN side of the call such as a DTMF keypad or hookswitch information. The UII message transmits the hookflash and DTMF signal information on the IP side of the call.
The hookflash is a common input indicating a brief on-hook condition that occurs during a call. For example, during a call, the phone user quickly depresses and then releases the hook on their telephone. It is not long enough in duration to be interpreted as a signal to disconnect the call; however, telephone switches and PBXs are frequently programmed to intercept hookflash indications and use them to allow a user to invoke supplemental services. For example, your local service provider may allow users to enter a hookflash to switch between calls if the user subscribes to a call waiting service.
To enable the CSP to transmit the PPL Event Indication message to the host, you must set Configuration Byte 1 for PPL Component L3P H.225 (0xA1) to 0x01. To disable, set the configuration byte to 0x00.
See the following PPL Component in this chapter.
PPL Component for H.225 - 0x00A1
The following data ICBs support the User Input Indication message. See the following in the ICB Chapter in the API Reference:
0x5B IP Signaling Series 3 Card ID
0x5C H.323 Hookflash Received (no data)
0x5D H.323 DTMF Signal Input Received
0x5E H.323 Signal Update Input Received
0x5F H.323 Alphanumeric Input Received
0x62 Remote Endpoints UII Capabilities
The CSP supports multiple alias addresses such as E.164, H.323Id, URL, and e-mail for the IP Signaling Series 3 card and remote H.323 endpoints.
The following TLVs support alias addressing:
0x02C1 Vendor ID
0x02C4 Gateway E164
0x02C6 Gateway URL ID
0x02C7 Gateway E-mail ID
0x27C4 Source IP
0x27C5 Source Port
0x27D8 Source H.323 ID
0x27D9 Source URL
0x27DA Source E-mail
0x27DC Remote H.323 ID
0x27DD Remote URL
0x27DE Remote E-mail
Gatekeeper Support
The CSP interfaces to gatekeepers from leading companies. This feature requires the CSP to send a gateway technology prefix in the registration request (RRQ). Use this prefix to configure the gateway's routing table or database in the gatekeeper. Include the new TLV below in the VoIP Protocol Configure message to create and send the prefix.
0x02D3 Gateway Technology Prefix
In this CSP H.323 implementation, the following specifications are supported:
H.225.0 (RAS, Q.931, RTP/RTCP)
H.245 and audio codecs
The VDAC-ONE or IP Network Interface Series 2 card provides the RTP stream for the H.323 call.
The H.323 software gets the RTP Payload Type and Payload size from the Route Table or Route Control message. If the type and size are not specified in either of those, the H.323 software uses the defaults.
Call Progress and Alerting Messages
The Progress message is an optional Q.931 call setup message. It can be sent by an H.323 gateway to indicate the progress of a call when interworking with a Switched Circuit Network (SCN). This message can also be sent by an H.323 endpoint before the Connect message is sent, depending on the supplementary service interaction.
On an H.323 call, Call Alerting and Progress messages can contain a Progress Indicator Information Element (IE) to describe an event that occurred during the life of the call. The CSP will establish a voice path when required.
The CSP does the following:
Processes an optional Progress message on an outgoing call.
Determines if the Q.931 Progress Indicator IE is present in the Alerting or Progress messages on a call.
Sends a PPL event indication to the host when the CSP receives an Alerting or Progress message. A message is sent to the
VDAC-ONE (or IP Network Interface Series 2) card to establish the voice path.
Receives a PPL Event Request of Alerting or Progress from the host with the progress indicator.
Transmits a Progress message to network.
Transmits the appropriate Release Complete Reason in Release Complete message to the network. The new Release Cause Codes are listed in the Release Cause Code TLV (0x27E3) in the Tag Length Value Blocks chapter in the API Reference.
This functionality works in gateway or normal (non-gateway) mode.
Dual Ethernet Port
You can configure the second Ethernet port on the
IP Signaling Series 3 card to separate the H.323 signaling traffic from the host control traffic. Cantata recommends having the host-to-CSP traffic carried on Ethernet port A and the H.323 signaling traffic carried on the Ethernet port B.
The BOOTP server is required to configure Ethernet port B.
The additional information is carried in the vendor specific area of the BOOTP response. You modify the BOOTP configuration to include new entries to carry the IP Address, Gateway IP Address, and Subnet Mask for the second physical Ethernet port.
Configuring the second Ethernet port is optional but if you enter an IP Address for Ethernet port B you must enter an associated Subnet Mask.
Important! Although a gateway IP Address may be configured for both Port A and Port B, only one is utilized. If two gateway IP addresses are configured, one for Port A and one for Port B the one specified for Port A will be used. Therefore, Cantata recommends that you configure only one gateway IP Address and that it be on Port B.
If you do not configure the second ethernet port, it is internally set to the same values configured for the first ethernet port.
For the associated procedure, refer to Configuring Dual Ethernet Ports on IP Signaling Card in the Application Development chapter in the Developer Guide: Overview.
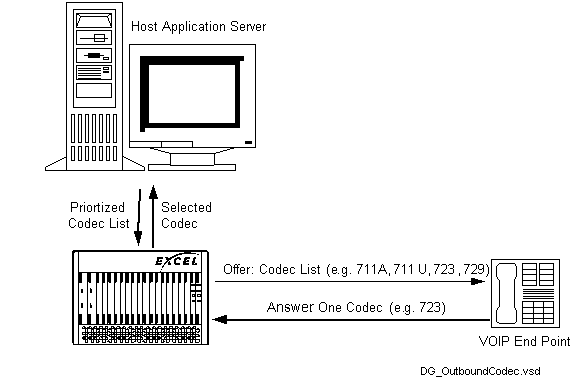
Codec List in H.323-Initiated Offers
The CSP can send a list of up to five supported codecs in an H.323 offer to an endpoint when establishing a media session. The receiving endpoint selects one codec from that list and reports the selection back in the answer message to the CSP.
The following applies to this feature:
The codec list is applicable for calls that use SIP or H.323 signaling and is not for clear-channel VoIP calls. For SIP signaling refer to Codec List in SIP-Initiated Offer.
The IP Network Interface card must use Profile 2.
The VDAC-ONE card must use Profile 0.
Without this feature, the call might not get established because the CSP could include a codec type that endpoint will not accept.
The figure below provides an overview of this process.
Figure 8-1 Codec List in Offer

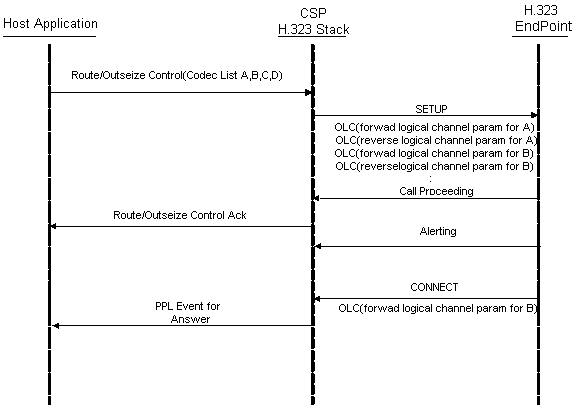
Outseize Control messages
The host application provides the codec list and sends the list in the Outseize Control message as shown in Host Provides Codec List:
Figure 8-2 Host Provides Codec List
TLVs Used
Use the following TLVs in the Outseize Control message to include the codec types:
0x29FF - Local End-Point Media Info
0x2A0E - Media Connection Address
0x2A01 - Per Media Stream Information
0x2A03 - Media Type
0x2A07 - Media Port
0x2A02 - Per Codec Info
The Outseize Control Message Trace shows how to use these TLVs in the Outseize Control message. Note that the Outseize Control message cannot exceed 260 bytes.
Important! DO NOT use the following TLVs for these codec types:
0x0100 - RTP Payload Type
0x0101 - RTP Payload Size
0x27B0 - RTP Payload Type
0x27B1 - RTP Payload Size
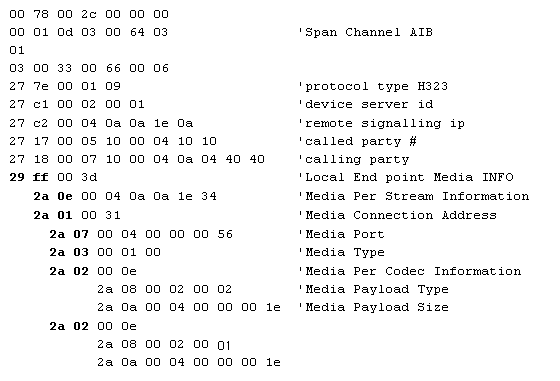
Outseize Control Message Trace
The following trace for the Outseize Control message shows the nested TLVs containing the codec information.
H.323 Host Control Direct and Gatekeeper Routed Calls
The H.323 protocol resident in the IP Signaling Series 3 card enables the CSP (gateway) to communicate with other H.323 gateways and gatekeepers in the call server network architecture.
Prior to this feature, the Gateway (CSP) supported either gateway (direct calls) or gatekeeper routed calls at any one time. When the Gateway (CSP) was registered with a gatekeeper it would process all the calls as Gatekeeper routed calls.
Starting with Release 8.4.0, if the CSP is registered with a Gatekeeper the CSP may send an ARQ (Admission Request) message to the Gatekeeper to request information about a remote endpoint. If the CSP chooses to send an ARQ to the gatekeeper, when the gatekeeper responds with the ACF (Access Confirmed), the response will determine if the CSP sends the call to the gatekeeper or directly to the remote endpoint.
Direct Routed
If the remote endpoint IP address TLV 0x27C2 is included in the Route Control/Outseize message, then the CSP will send the call to the remote endpoint IP address that is specified in the TLV 0x27C2. The CSP will not send the ARQ to the gatekeeper.
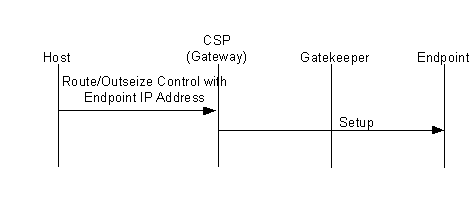
Gatekeeper Routed
If the remote endpoint IP Address TLV 0x27C2 is omitted from the Route Control or Outseize Control message, then the CSP sends the ARQ message to the Gatekeeper. When the ACF is returned, the CSP looks in the message to determine where to send the call. The CSP will send the call either to the remote endpoint IP address provided by the gatekeeper or to the gatekeeper as specified in the ACF message.
The end result is the CSP does not actually modify the gatekeepers behavior. The CSP acts differently based upon data included in the Route Control/ Outseize Control message.
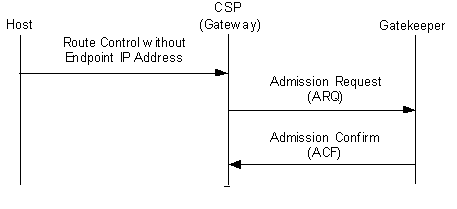
Invoking
To invoke this feature use the Route Control (0x00E8) message with the Remote End Signaling IP Address (Q.931) (0x 27C2) TLV. This TLV provides the remote endpoint IP address for the call. This TLV will be used for each call to determine whether the ARQ and ACF message exchanged is implemented for that call.
Important! The Remote End Signaling Port (Q.931) (0x27C3) TLV specifies the remote signaling port. The defaults are: port number 1719 for gatekeeper routed calls and port number 1720 for gateway routed calls. This TLV is only necessary when using non-standard values.
H.245 Tunneling
The H.245 is a control signaling protocol in the H.323 multimedia communication architecture used to exchange end-to-end H.245 messages such as:
master/slave determination
capability exchange
logical channel procedures
This configurable CSP H.245 Tunneling feature permits the encapsulation of H.245 messages within H.225 message between H.323 endpoints.
Enabling
To enable H.245 Tunneling for the IP Signaling card, use the H.245 Tunneling Configure TLV (0x02D5) in the VoIP Protocol Configure message (0x00EE). Refer to the TLV chapter in the API Reference.
Inbound and Outbound calls
The IP Signaling cards can then accept incoming calls with H.245 tunneling. With this feature enabled on the IP Signaling card, H.245 tunneling can be used on a per outbound call basis by using the H.245 Outbound Tunneling TLV (0x27E4) in Route Control or Outseize Control messages.
Note that if tunneling is not enabled on the IP Signaling card using the H.245 Tunneling Configure TLV (0x02D5) in the VoIP Protocol Configure message, then the CSP cannot offer outbound tunneling calls.
Configuring with CSA
Refer to the Configuring H.323 in the Converged Services Administrator Users Guide.