Home > Hosting media buffering and formatting > Formatting media buffers for pass-through channels
The proprietary NMS packetized format defines the structure of the data passed between the application and the ADI multimedia functions on play and record for pass-through channels.
|
Operation |
Description |
|
Play |
The application reads the audio/video files from disk, loads the streams onto host memory, and calls adiPlayMMFromMemory or adiPlayMMAsync one time each for video and audio, using the corresponding buffer sizes and pointers. |
|
Record |
The application allocates two host memory buffers to receive the complete recorded streams, and calls adiRecordMMToMemory or adiRecordMMAsync one time each for video and audio, using the corresponding buffer sizes and pointers. |
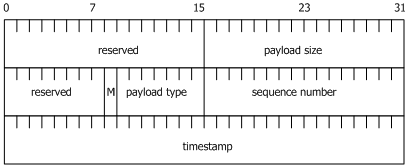
The data within the audio and video buffers consist of a sequence of packets arranged in the order in which they were received (recorded) or to be delivered (played). The packet header is referred to as the NMS packetized header (and is similar to an RTP header):

The second reserved field (8 bits) is the NMS magic number and is set to 0xD.
For audio channels, the timestamps are 8000/sec. This originates from the standard 8 kHz audio sampling rate.
For video channels, the timestamps are 90000/sec. This originates from the standard 90 kHz video sampling rate.
For video NMS headers, the payload size is not constant because the video bit rate is variable.
For audio NMS headers, the payload size depends on the coding rate chosen for AMR or G.723 encoding, or whether G.711 is being used.
It may not be constant if the DTX function (voice activity detection + comfort noise generation) is enabled on the audio encoder. In this case, when silence is detected, the audio encoder can generate non-speech frames, such as Silence Insertion Descriptor (SID) frames.
Payload types qualify the media encoding of the payload, comply with the standard profiles, and use by default, the values defined by RFC 3551, where applicable. During a play operation RTP packets are transmitted with the payload type value taken directly from the NMS-packetized header.
When the audio and video buffers are generated by the Multimedia File Interface library functions, the application can control the values of payload types.
The RTP payload for each RTP packet is located after the NMS header. The RTP payload can contain a media specific header:
For each H.263 RTP packet, the RTP payload consists of the H.263 payload header (either per RFC 2190 or RFC 2429) followed by the H.263 compressed bit stream.
For each H.264 RTP packet, the RTP payload does not contain a media specific header, but contains the H.264 compressed bit stream only.
For each MPEG-4 RTP packet, the RTP payload does not contain a media specific header, but contains the MPEG-4 compressed bit stream only.
For audio the payload contains only the audio bit stream.